Refactor the release implementation into a dedicated workflow module with clear separation of concerns. Enforce a safe, deterministic Git flow by always syncing with the remote before modifications, pushing only the current branch and the newly created version tag, and updating the floating *latest* tag only when the released version is the highest. Add explicit user prompts for confirmation and optional branch deletion, with a forced mode to skip interaction. Update CLI wiring to pass all relevant flags, add comprehensive unit tests for the new helpers and workflow entry points, and introduce detailed documentation describing the release process, safety rules, and execution flow.
Package Manager 🤖📦
Kevin's Package Manager (PKGMGR) is a multi-distro package manager and workflow orchestrator. It helps you develop, package, release and manage projects across multiple Linux-based operating systems (Arch, Debian, Ubuntu, Fedora, CentOS, …).
PKGMGR is implemented in Python and uses Nix (flakes) as a foundation for distribution-independent builds and tooling. On top of that it provides a rich CLI that proxies common developer tools (Git, Docker, Make, …) and glues them together into repeatable development workflows.
Why PKGMGR? 🧠
Traditional distro package managers like apt, pacman or dnf focus on a
single operating system. PKGMGR instead focuses on your repositories and
development lifecycle:
- one configuration for all your repos,
- one CLI to interact with them,
- one Nix-based layer to keep tooling reproducible across distros.
You keep using your native package manager where it makes sense – PKGMGR coordinates the development and release flow around it.
Features 🚀
Multi-distro development & packaging
-
Manage many repositories at once from a single
config/config.yaml. -
Drive full release pipelines across Linux distributions using:
- Nix flakes (
flake.nix) - PyPI style builds (
pyproject.toml) - OS packages (PKGBUILD, Debian control/changelog, RPM spec)
- Ansible Galaxy metadata and more.
- Nix flakes (
Rich CLI for daily work
All commands are exposed via the pkgmgr CLI and are available on every distro:
-
Repository management
clone,update,install,delete,deinstall,path,list,config
-
Git proxies
pull,push,status,diff,add,show,checkout,reset,revert,rebase,commit,branch
-
Docker & Compose orchestration
build,up,down,exec,ps,start,stop,restart
-
Release toolchain
version,release,changelog,make
-
Mirror & workflow helpers
mirror(list/diff/merge/setup),shell,terminal,code,explore
Many of these commands support --preview mode so you can inspect the
underlying Git or Docker calls without executing them.
Full development workflows
PKGMGR is not just a helper around Git commands. Combined with its release and versioning features it can drive end-to-end workflows:
- Clone and mirror repositories.
- Run tests and builds through
makeor Nix. - Bump versions, update changelogs and tags.
- Build distro-specific packages.
- Keep all mirrors and working copies in sync.
The extensive E2E tests (tests/e2e/) and GitHub Actions workflows (including
“virgin user” and “virgin root” Arch tests) validate these flows across
different Linux environments.
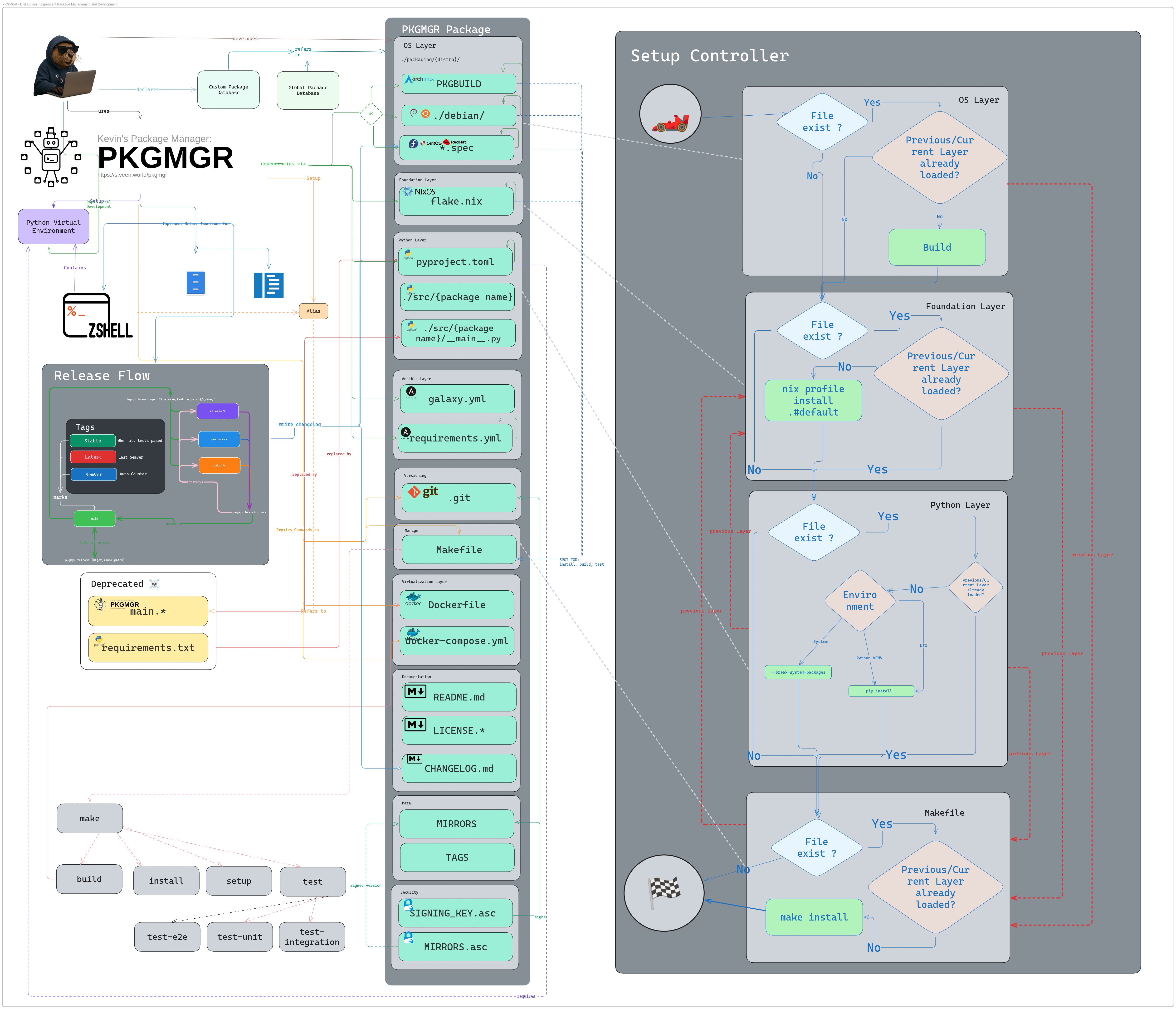
Architecture & Setup Map 🗺️
The following diagram gives a full overview of:
- PKGMGR’s package structure,
- the layered installers (OS, foundation, Python, Makefile),
- and the setup controller that decides which layer to use on a given system.
Diagram status: 11 December 2025 Always-up-to-date version: https://s.veen.world/pkgmgrmp
Installation ⚙️
1. Get the latest stable version
For a stable setup, use the latest tagged release (the tag pointed to by
latest):
git clone https://github.com/kevinveenbirkenbach/package-manager.git
cd package-manager
# Optional but recommended: checkout the latest stable tag
git fetch --tags
git checkout "$(git describe --tags --abbrev=0)"
2. Install via Make
The project ships with a Makefile that encapsulates the typical installation flow. On most systems you only need:
# Ensure make, Python and pip are installed via your distro package manager
# (e.g. pacman -S make python python-pip, apt install make python3-pip, ...)
make install
This will:
- create or reuse a Python virtual environment,
- install PKGMGR (and its Python dependencies) into that environment,
- expose the
pkgmgrexecutable on your PATH (usually via~/.local/bin), - prepare Nix-based integration where available so PKGMGR can build and manage packages distribution-independently.
For development use, you can also run:
make setup
which prepares the environment and leaves you with a fully wired development workspace (including Nix, tests and scripts).
Usage 🧰
After installation, the main entry point is:
pkgmgr --help
This prints a list of all available subcommands, for example:
pkgmgr list --all– show all repositories in the configpkgmgr update --all --clone-mode https– update every repositorypkgmgr release patch --preview– simulate a patch releasepkgmgr version --all– show version information for all repositoriespkgmgr mirror setup --preview --all– prepare Git mirrors (no changes in preview)pkgmgr make install --preview pkgmgr– preview make install for the pkgmgr repo
The help for each command is available via:
pkgmgr <command> --help
License 📄
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.
Author 👤
Kevin Veen-Birkenbach https://www.veen.world